Risk management is an increasingly important business driver and stakeholders have become much more concerned about risk.Risk may be a driver of strategic decisions, it may be a cause of uncertainty in the organization or it may simply be embedded in the activities of the organization which can have consequences in terms of economic performance and professional reputation. The growth of a business for any organization depends mainly on the effective risk management system being implemented to to help organizations perform well in an environment full of uncertainty. The strategy that most of the organization implement to manage risks are,
However, the main challenge here is to identify and implement a suite of solutions to be able to integrate at all levels of an enterprise operations and continually improving risk management throughout the organization. Execution of these activities in a way that actually and demonstrably improves the ability of the organization to meet its objectives in a repeatable fashion is the ultimate aim of any Risk Management System.

A set of components that support and sustain risk management that can help organizations to increase the likelihood of achieving objectives, improve the identification of opportunities and threats and effectively allocate and use resources for risk treatment.
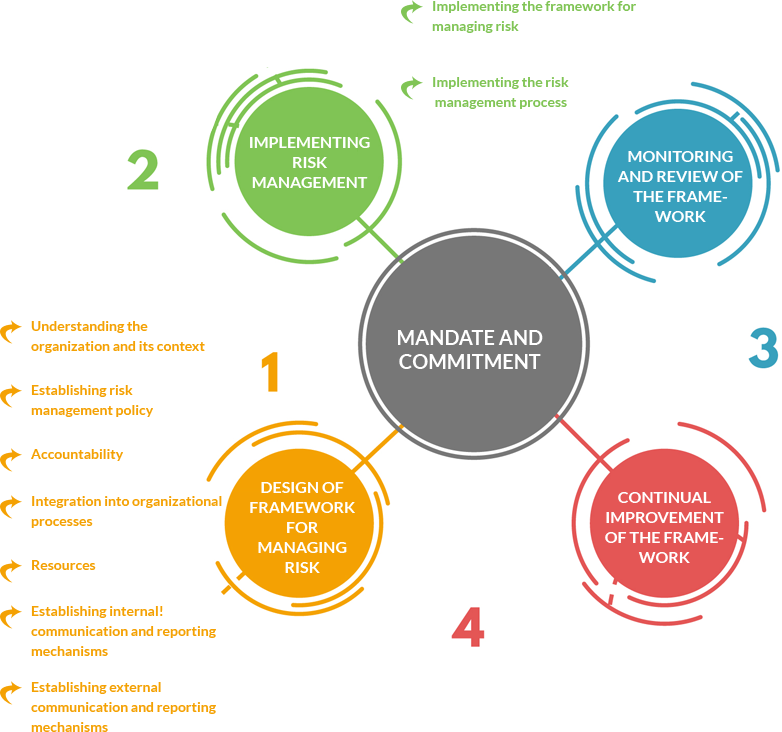
The ISO 31000 is a framework which is implemented for effective management of risks rather than supporting the process of risk management. An organization, based on its requirement over the risk management, describes in detail about the framework centered on the risk architecture, strategy and protocols that is actually followed by them. The risk strategy should be that, an organization’s risk management system should achieve the objectives what they are seeking for. It is supported by the risk protocols which in detail describes the procedures to implement the strategy to manage risk effectively. Being an initial component of the ISO 31000 “Mandate and Commitment”, the framework consists of the essential steps that needs to be followed in the implementation and ongoing support of any risk management process. They are,
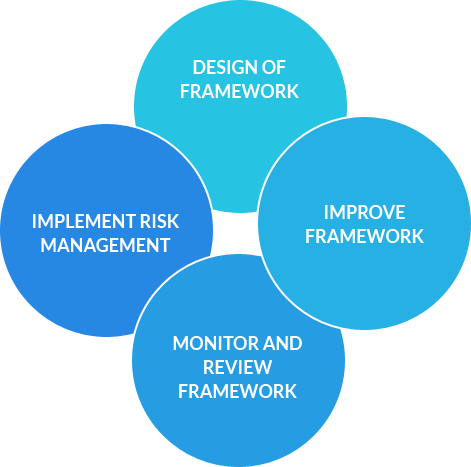
Below is the strategic structure which represents the internal arrangements for ease of communicating on risk issues and sets out the roles and responsibilities of the individuals and committees that support the risk management process.
Off late, the definition of risk‘the chance of something happening that will have an impact on objectives’ has changed to ‘the effect of uncertainty on objectives’. While risk managers will continue to consider the possibility of risks occurring, they should now apply risk treatment options to ensure that the uncertainty of their agency meeting its objectives will be avoided, reduced, removed or modified and/or retained. Some of the Principles that requires to be highlighted when it comes to risk management are:
The essence of an effective risk management system is to achieve an agency’s objectives through an unremitting review of its process and systems
Its is highly recommended for an agency’s governance framework to be integrated with the risk management system and become a part of its planning processes, at all levels of enterprise operations and strategies.
The process of risk management assists decision makers to make informed choices, identify priorities and select the most appropriate action.
It provides the organizations with highly viable opportunities to identify potential risks and implement suitable solutions to maximize the chance of gain while minimizing the chance of loss.
In, order to ensure efficiency, consistency and the reliability of results the process of risk management should be streamlined across an agency.
For an effective risk management skill, it is important to understand and consider all available information relevant to an activity and to be aware that there may be limitations on that information. It is then important to understand how all this information informs the risk management process.
An agency’s risk management framework needs to include its risk profile, as well as take into consideration its internal and external operating environment.
Risk management needs to recognize the contribution that people and culture have on achieving an agency’s objectives.
Engaging stakeholders, both internal and external, throughout the risk management process recognizes that communication and consultation is key to identifying, analyzing and monitoring risk.
The process of managing risk needs to be flexible. The challenging environment we operate in requires agencies to consider the context for managing risk as well as continuing to identify new risks that emerge, and make allowances for those risks that no longer exist.
ISO 31000:2018 can be applied throughout the life of an organization, and to a wide range of activities, including strategies and decisions, operations, processes, functions, projects, products, services and assets. ISO 31000:2018 can be applied to any type of risk, whatever its nature, whether having positive or negative consequences. The design and implementation of risk management plans and frameworks will need to take into account the varying needs of a specific organization, its particular objectives, context, structure, operations, processes, functions, projects, products, services, or assets and specific practices employed.
It is intended that ISO 31000:2018 be utilized to harmonize risk management processes in existing and future standards. It provides a common approach in support of standards dealing with specific risks and/or sectors, and does not replace those standards.It is to be noted that, ISO 31000:2018 is not intended for the purpose of certification.
Communication and consultation with internal and external stakeholders, to gain their input to the process and their ownership of the outputs. It is highly important to understand the objectives of stakeholders’ in order to plan their involvement thereby, considering thier views in setting risk criteria.
Monitoring and review, so that appropriate action plans are deviced against new risks that emerge due to changes in either the organizations objectives or the internal and external environment in which they pursue. However, this involves environmental scanning by risk owners, control assurance, taking on board new information that becomes available, and learning lessons about risks and controls from the analysis of successes and failures.
The central spine of the risk management process is concerned with preparing for and then conducting risk assessment leading to risk treatment. The process starts through defining what the organisation wants to achieve and the external and internal factors that may influence success in achieving those objectives. This step is called establishing the context and is an essential precursor to risk identification.

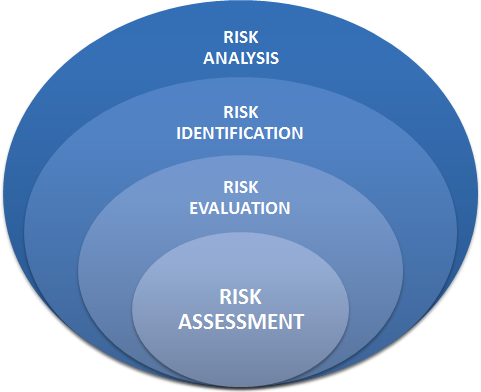
This requires the application of a systematic process to understand what could happen, how, when, and why. The confidence in determination of the level of risk and its sensitivity to preconditions and assumptions should be considered in the analysis, and communicated effectively to decision makers and, as appropriate, other stakeholders.
In ISO 31000, risk analysis is concerned with developing an understanding of each risk, its consequences, and the likelihood of those consequences. Whether the end result is expressed as a qualitative, semi quantitative, or quantitative manner, gaining this understanding requires consideration of the effect and reliability of existing controls and any control gaps. The way in which consequences and likelihood are expressed and the way in which they are combined to determine a level of risk should reflect the type of risk, the information available, and the purpose for which the risk assessment output is to be used.
It involves making a decision about the level of risk and the priority for attention through the application of the criteria developed when the context was established. Risk treatment: It is the process by which existing controls are improved or new controls are developed and implemented. It involves evaluation of and selection from options, including analysis of costs and benefits and assessment of new risks that might be generated by each option, and then prioritising and implementing the selected treatment through a planned process. There is a great deal of iteration between risk evaluation and risk treatment as each set of risk treatment options is tested until the preferred set is found that yields the greatest benefit.
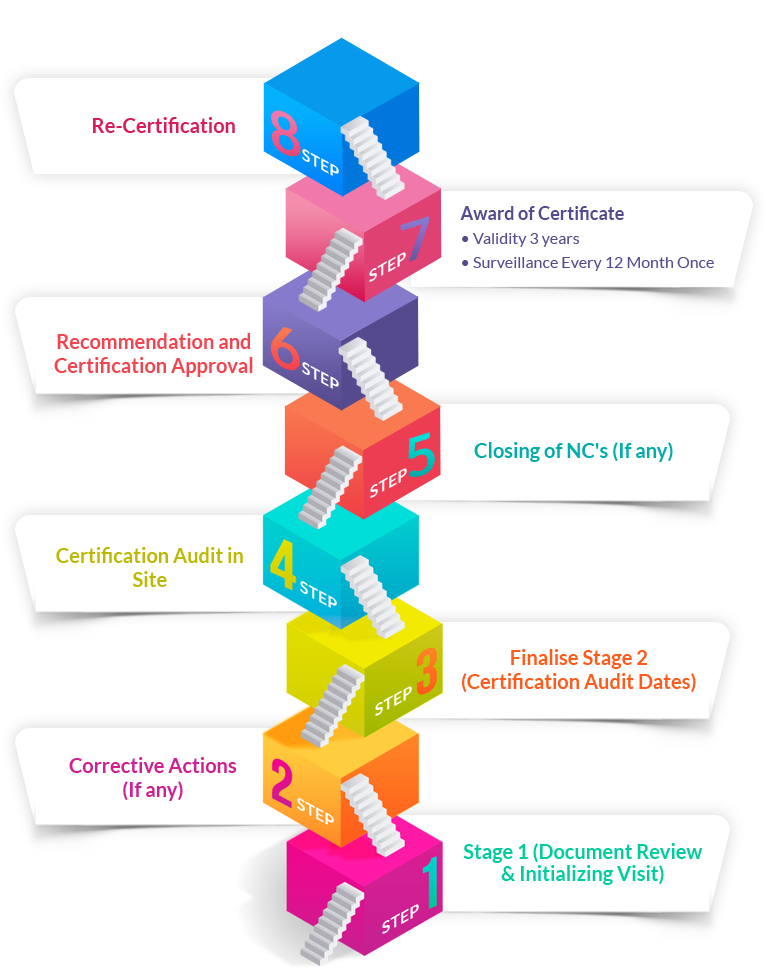
You can transfer the certificate at any stage to us during surveillance/ recertification.
To transfer any certificate IAF has laid down New rules –
So what I need to DO.
At TRAIBCERT ,our mission is to create a more resilient and sustainable risk management system global society through a better understanding of possible risks that are catastrophic. Through TRAIBCERT’s Risk Management service, we facilitate the identification, analysis, monitoring, review and treatment of both existing and potential hazards and risks throughout your organization.
With our policies aligned with the requirements for the ISO 31000 Risk Management standard, we will give your organization a strategic advantage in managing, mitigating and preventing risk in your business.